Spacemacs layers list
Table of ContentsClose
- 1. Description
- 2. Chats
- 3. Checkers
- 4. Completion
- 5. E-mail
- 6. Emacs
- 7. File trees
- 8. Fonts
- 9. Fun
- 10. Internationalization
- 11. Miscellaneous
- 11.1. Copy-as-format
- 11.2. Dtrt-indent
- 11.3. Ietf
- 11.4. Multiple-cursors
- 11.5. Nav-flash
- 11.6. Parinfer
- 11.7. Spacemacs-completion
- 11.8. Spacemacs-defaults
- 11.9. Spacemacs-editing
- 11.10. Spacemacs-editing-visual
- 11.11. Spacemacs-evil
- 11.12. Spacemacs-language
- 11.13. Spacemacs-layouts
- 11.14. Spacemacs-misc
- 11.15. Spacemacs-modeline
- 11.16. Spacemacs-navigation
- 11.17. Spacemacs-org
- 11.18. Spacemacs-project
- 11.19. Spacemacs-purpose
- 11.20. Spacemacs-visual
- 12. Music
- 13. Operating systems
- 14. Pair programming
- 15. Programming languages
- 16. Readers
- 17. README.org files that need proper tags
- 18. Source control
- 19. Spacemacs
- 20. Tagging
- 21. Themes
- 22. Tools
- 22.1. Ansible
- 22.2. Apache
- 22.3. Bm
- 22.4. CFEngine
- 22.5. Chrome
- 22.6. CMake
- 22.7. Command-log
- 22.8. DAP
- 22.9. Debug
- 22.10. Docker
- 22.11. Eglot
- 22.12. Eww
- 22.13. EXWM
- 22.14. Fasd
- 22.15. Finance
- 22.16. Geolocation
- 22.17. Imenu-list
- 22.18. Import-js
- 22.19. Kubernetes
- 22.20. LSP
- 22.21. Meson
- 22.22. Nginx
- 22.23. Node
- 22.24. Pandoc
- 22.25. Pass
- 22.26. Prettier
- 22.27. Prodigy
- 22.28. Puppet
- 22.29. Ranger
- 22.30. Rebox
- 22.31. Restclient
- 22.32. Saltstack
- 22.33. Shell
- 22.34. Sphinx
- 22.35. Systemd
- 22.36. Tern
- 22.37. Terraform
- 22.38. Tide Layer
- 22.39. Tmux
- 22.40. Translate Layer
- 22.41. Transmission
- 22.42. Tree-sitter
- 22.43. Vagrant
- 22.44. Web-beautify
- 22.45. Xclipboard
- 23. Vim
- 24. Web services
1. Description
THIS FILE IS AUTO-GENERATED! Don't edit it directly. See "README.org tags" section of CONTRIBUTING.org for the instructions.
This is an overview of Spacemacs configuration layers. For information about configuration layer development see Configuration layers development.
2. Chats
2.1. ERC
Layer for ERC IRC chat.
Features:
- Highlight nicks (using erc-hl-nicks)
- Image inline support (using erc-image)
- Logging to
~/.emacs.d/.cache/erc-logsandViewLogModefor viewing logs (using erc-view-log) - YouTube videos Thumbnails inline (using erc-yt)
- Social Graph for ERC messages (using erc-social-graph)
- Optional SASL authentication via the variable
erc-enable-sasl-auth(using erc-sasl) - D-BUS notifications via the variable
erc-enable-notifications - Completion of Emojis using company-emoji (still needs a way of showing, either
using the
emojilayer or having a proper font) :clap:
2.2. Jabber
This layer adds support for the Jabber (XMPP) client for Emacs
Features:
- Use Jabber without having to leave Spacemacs
2.3. RCIRC
This layer provide support for rcirc with optional support for authinfo and ZNC.
Features:
- Store channel logs into
~/.emacs.d/.cache/rcirc-logs/<channel> - Support for credentials stored in
~/.authinfo.gpg(need to have gnutls) - Support ZNC support (with optional
~/.authinfo.gpg) - Colored nicknames
- Real-time change when people use
s/foo/bar/in chat - Completion of Emojis using company-emoji (still needs a way of showing, either
using the
emojilayer or having a proper font) :clap:
2.4. Slack
This layer provides an interface to the Slack chat service via the emacs-slack package. Where possible, this layer aims to reuse key bindings from the IRC packages in Spacemacs.
Features:
- Real time messaging with emacs-websocket
- Connect to multiple slack instances
- Notifications with alert.el
3. Checkers
3.1. Spell Checking
+checkers/spell-checking/README.org
This layer provides spell checking capabilities to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Buffer-wide spell checking via external command (ispell, hunspell, aspell) run through Flyspell.
- Spell as you type
- Optional correction popups, controlled by
enable-flyspell-auto-completionvariable. - Auto dictionary mode for some languages.
3.2. Syntax Checking
+checkers/syntax-checking/README.org
This layer adds on-the-fly syntax checking to all supported language layers.
Features:
- Automatic syntax checking with Flycheck for various language layers.
- Shows syntax error in pop-up window via flycheck-pos-tip.
4. Completion
4.1. Auto-completion
+completion/auto-completion/README.org
This layer adds auto-completion to all supported language layers.
Features:
- Support for code completion with company or auto-complete for various language layers
- Frequency-based suggestions via company-statistics for
company - Integration with yasnippet and auto-yasnippet
- Automatic configuration of hippie-expand
- Automatic docstring tooltips are provided by company-quickhelp
4.2. Compleseus
+completion/compleseus/README.org
This layer implements completion provided by combining the following packages:
selectrumorvertico: vertical completion user interfaceconsult: useful commands usingcompleting-readembark: provides minibuffer actionsmarginalia: annotations to completion candidatesorderless: filtering enhancements
It only supports emacs 27 or later.
Features:
- Similar features like
ivyorhelm
4.3. Helm
This layer enables Helm everywhere in Spacemacs. The alternative to this layer is the Ivy layer which brings the same level of integration as Helm.
These completion systems are the central control towers of Spacemacs, they are used to manage buffers, projects, search results, configuration layers, toggles and more…
Mastering your choice of completion system will make you a Spacemacs power user.
Features:
- Project wide
greplike text search viahelm-dir-smart-do-search - Project wide text replacements using
helm-edit-mode - Buffer wide dynamic text search via
helm-swoop - Fuzzy matching for most
helm-sources - Detailed configuration parameters for helms appearance
- Intuitive
transient state
4.4. Ivy
This layer enables Ivy for completion. It will replace the default completion by Helm.
These completion systems are the central control towers of Spacemacs, they are used to manage buffers, projects, search results, configuration layers, toggles and more…
Mastering your choice of completion system will make you a Spacemacs power user.
Features:
- Project wide
greplike text search viasearch-auto - Project wide text replacements using
counsel-imenu - Buffer wide dynamic text search via
swiper - Detailed configuration parameters for ivy appearance
- Intuitive
transient state - Advanced buffer information with
ivy-rich
4.5. Templates
+completion/templates/README.org
This layer provides templates to Spacemacs. A template consists of text that is automatically inserted into a new file when it is opened. This is done via yatemplate, which leverages yasnippet.
Features:
- Auto-insert snippets when creating specific new files.
5. E-mail
5.1. Gnus
This layer integrates a general purpose email/newsgroup client into Spacemacs.
Features:
5.2. Mu4e
This layer adds support for the Mu4e email client.
Features:
- Search, read, reply, move, and delete email.
- Search-based: no folders, only queries.
- UI optimized for speed: quick keystrokes for common actions.
- Very extendable and customizable.
- Integration with Helm.
- Maildir summary.
- Notifications using mu4e-alert.
5.3. Notmuch
Notmuch offers a fast, global-search and tag-based email system to use within your text editor or in a terminal.
This layer integrates the Notmuch Emacs package into Spacemacs.
Features:
- Email searching
- Email tagging
6. Emacs
6.1. Better Defaults
+emacs/better-defaults/README.org
This layer enhances the default commands of Emacs and is primarily intended to
be used with the emacs editing style as it does not change anything in the Vim
key bindings.
However the emacs editing style is not required. You can still use this layer
while you are using the vim editing style if you have some kind of mixed
style, but some of the layer bindings might be shadowed by the evil key bindings.
The commands defined in this layer are taken from various sources like Prelude.
Features:
- Smart line navigation: Subsequent presses of
C-atoggles between the beginning of the line and the first non-whitespace character. Similarly, subsequent presses ofC-ewill toggle between the end of the code and the end of the comments. spacemacs/backward-kill-word-or-region: A combination ofkill-regionandbackward-kill-word, depending on whether there is an active region. If there's an active region kill that. If not kill the preceding word.- Fill or unfill paragraph: Pressing
M-qfor the first time fills current paragraph and pressingM-qfor the second time unfills it. Note that some modes override this key binding so it's not available everywhere. Due to implementation details unfilling doesn't work when called twice viaM-x.
6.2. Helpful
This layer replaces the existing emacs related help buffers with more detailed ones.
Features:
- Better help buffers with helpful for emacs related buffers
- Source code shown implicitly in help buffer for all lisp objects
- More detailed descriptions in the emacs specific function, variable and key help buffers
- Better formatted elisp docstrings
6.3. IBuffer
This layer configures Emacs IBuffer for Spacemacs.
Features:
- Grouping of buffers by major-modes
- Grouping of buffers by projects
6.4. Org
This layer enables org mode for Spacemacs.
Features:
- Vim inspired key bindings are provided by evil-org-mode
- Nicer bullet via org-superstar-mode
- A pomodoro method integration via org-pomodoro
- Presentation mode via org-present
- Insertion of images via org-download
- Project-specific TODOs via org-projectile
- Easy insert of URLs from clipboard with org format via org-cliplink
- Rich insert of code (into a source block with highlighting, and a link) from other buffers via org-rich-yank
- Pixel-perfect visual alignment for Org and Markdown tables via valign
- Text transclusion via org-transclusion
6.5. Outshine
6.6. Quickurl
Quickurl is a package in vanilla emacs for saving and inserting URLs. These are key bindings for the various methods of insertion, which are not bound by default.
Features:
- Key bindings to dispatch Quickurl (which is in vanilla Emacs).
6.7. Semantic
CEDET is a *C*ollection of *E*macs *D*evelopment *E*nvironment *T*ools written with the end goal of creating an advanced development environment in Emacs. CEDET includes common features such as intelligent completion, source code navigation, project management, code generation with templates. CEDET also provides a framework for working with programming languages; support for new programming languages can be added and use CEDET to provide IDE-like features. This framework is called Semantic.
Semantic is a package that provides a framework for writing parsers. Parsing is a process of analyzing source code based on programming language syntax. The packages relies on Semantic for analyzing source code and uses its results to perform smart code refactoring that based on code structure of the analyzed language, instead of plain text structure. Semantic is the core of CEDET.
Features:
- Display function or variable definition at the bottom.
- Support common C/C++ refactoring with semantic-refactor. See this page for demonstration of refactoring features.
- Support Lisp source code formatting with semantic-refactor. See this page for demonstration of Lisp formatting features.
6.8. Smex
This layer provides a more traditional alternative to helm-M-x based on ido.
Features:
- Provides an alternative way for
helm-M-xbased onidoand smex
6.9. Tabs
This layer adds support for tabs. Implementation is done using Centaur Tabs.
Features:
- Sets up tabs using Centaur tabs as backend
- Optionally auto hide tabs after delay
6.10. Typography
This layer provides support for typographic text editing in Spacemacs.
Features:
- Modes to automatically insert and cycle among typographic characters
- Typo Mode automatically inserts and cycles among typographic Unicode characters on some keys.
- Tildify Mode automatically inserts non-breaking spaces where required (Only available on Emacs 25).
7. File trees
7.1. Neotree
This layer setups a file tree navigator buffer using Neotree (replacing the Treemacs layer).
Features:
- intuitive evil key bindings integration
- supports multiple themes
- transient state by pressing on
? - version-control integration
7.2. Treemacs
This layer sets up a file navigation and project explorer side-window via Treemacs.
Features:
A detailed overview of the features of Treemacs is available in the Treemacs readme. In short, Treemacs offers:
- Simple and powerful navigation and ability to detail exactly how and where a file should be opened.
- Good looking icons.
- Display of multiple file trees organized as projects residing in a workspace.
- Ability to show tags contained in files. Tags are provided by Imenu, so nearly every filetype is supported.
- Mouse interface for single and double left clicks in line with modern GUI standards (clicking on an icon will also display the file's tags).
- Location awareness: commands like
find-fileormagit-statuswill use the location of the node at point (with$HOMEas fallback). - Optional fontifying of files based on their git status.
- Optional collapsing of single-dir-child directories into one.
- Doing both asynchronously for an imperceptible performance cost.
- Optional
follow-modeto automatically focus the currently selected file or tag. - Optional
filewatch-modeto automatically refresh the view after (and only after) changes to the shown filesystem.
8. Fonts
8.1. Unicode-fonts
+fonts/unicode-fonts/README.org
This layer adds support for unicode-fonts package. It is recommended to install the fonts listed in the Quickstart section of the unicode-fonts README.
Features:
- Display Unicode glyphs using the best available font.
- Easily override glyphs or sections of glyphs.
- Display color emoji on both the macOS port version of Emacs and emacs-plus
(with
unicode-fonts-force-multi-color-on-macset to non nil). - Enable support for font ligature in Emacs 27 + via ligatures.el.
9. Fun
9.1. Emoji
This layer adds support for Emoji emoticons from emoji-cheat-sheet.
Features:
- Browse Emoji in a dedicated buffer
- Display Emoji images in buffer
- Insert one or several Emoji with a helm front-end
- Completion of Emojis using company-emoji
9.2. Games
This layer allows you to play evilified games in Spacemacs.
Features:
- 2048-game
- Pacmacs (Pacman for Emacs)
- Sudoku
- Tetris
- Typit
9.3. Selectric
This layer makes your Emacs sound like an IBM Selectric typewriter, for those moments when your loud, clicky mechanical keyboard is not at hand, yet, you'd still wish to enjoy the sound.
Features:
- Brings back fond memories about your first programming job where you started with that big mechanical keyboard and the small monochrome display working on the latest IBM Iseries server.
9.4. Xkcd
This layer adds a xkcd navigation mode using emacs-xkcd.
Features:
- Load a random xkcd
- Show the text in the modeline
- Open explanation and current comic in browser
- Cache the comics in
.cache/xkcd
10. Internationalization
10.1. Chinese
This layer adds support for traditional Chinese script to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Support for the Pinyin (拼音) input method via chinese-pyim.
- Support for the Wubi (五笔) input method via chinese-wbim.
- Integration of the native input method framework fcitx via cute-jumper/fcitx.el.
- Integration of the Youdao (有道) Dictionary via youdao-dictionary.
- Support for file searches in
diredusing Chinese Pinyin characters via find-by-pinyin-dired. - Support for jumping to Chinese Pinyin characters with
ace-jump-modevia ace-pinyin. - Support for conversion between simplified and traditional Chinese texts via chinese-conv.
- Automatic visual separation of Chinese and Latin characters via coldnew/pangu-spacing.
- Automatic joining of consecutive Chinese lines into a single long line without unwanted space when exporting org-mode to html.
10.2. Japanese
This Layer adds Japanese related packages.
Features:
- evil-tutor-ja: Japanese Vimtutor adapted to Emacs+Evil and wrapped in a major mode
- migemo: Japanese incremental search through dynamic pattern expansion
- helm-migemo-mode: helm with migemo
- avy-migemo: avy with migemo
- ddskk: Simple Kana to Kanji conversion program (SKK)
- japanese-holidays: calendar functions for the Japanese calendar
- pangu-spacing: emacs minor-mode to add space between Japanese and English characters.
- Join consecutive Japanese lines into a single long line without unwanted space when exporting org-mode to html.
10.3. Keyboard-layout
+intl/keyboard-layout/README.org
This layer configures some key bindings in Spacemacs, to make it compatible with
keyboard layouts that differ from the traditional en-us QWERTY layout.
Features:
- Support alternative keyboard layouts within Spacemacs
- Remap navigation commands to the homerow of your chosen layout
- Remap missing commands automatically to elsewhere in the layout
11. Miscellaneous
11.1. Copy-as-format
+misc/copy-as-format/README.org
This layer adds support for copy-as-format.
Features:
- Function to copy buffer locations as GitHub/Slack/JIRA/HipChat/… formatted code
11.2. Dtrt-indent
This is a simple layer wrapping the dtrt-indent Emacs package for automatic detection and switching of indentation style.
It is automatically enabled using the method suggested here.
Features:
- Indentation style detection and automatic configuration to match file in open buffer.
11.3. Ietf
The IETF layer collects various useful packages for participating in the
Internet Engineering Task Force (https://www.ietf.org).
Features:
- Fetching and opening IETF documents.
- Viewing IETF documents.
- Writing IETF documents.
11.4. Multiple-cursors
11.6. Parinfer
This layer provides an implementation of parinfer, a lisp editing paradigm that controls indentation based on parentheses or vice versa.
Features:
- Automatic management of parenthesis in Clojure, Emacs Lisp, Common Lisp and Scheme following the parinfer editing paradigm.
- Powered by a native library in the background
11.7. Spacemacs-completion
+spacemacs/spacemacs-completion/README.org
This layer does basic setup for completion frameworks like helm, ivy and
ido.
Its main role is to ensure sane defaults and consistent UI between helm
and ivy because even when you are using only one of them you could still
need to use the other (for instance a package that supports only helm).
Advanced configuration of these packages can be found in their respective
layers in +completion layer directory.
Features:
- Base preconfiguration of
helmandivyfor other layers to use. - Basic support for
ido-navigationconfiguration and transient state.
11.8. Spacemacs-defaults
+spacemacs/spacemacs-defaults/README.org
This layer configures mostly Emacs built-in packages to given them better defaults.
Features:
- Configures packages:
- abbrev
- archive-mode
- bookmark
- conf-mode
- cus-edit
- dired
- dired-x
- display-line-numbers (only in Emacs 26.x and newer)
- electric-indent-mode
- easypg
- ediff
- eldoc
- hi-lock
- image-mode
- imenu
- occur-mode
- package-menu
- page-break-lines
- process-menu
- quickrun
- recentf
- savehist
- saveplace
- subword
- tar-mode
- uniquify
- url
- visual-line-mode
- whitespace
- winner
- zone
11.9. Spacemacs-editing
+spacemacs/spacemacs-editing/README.org
This layer adds packages to improve editing with Spacemacs.
Features:
- Support for automatic indentation of code via
aggressive-indent. - Support for jumping to chars using a decision tree via
avy. - Improvements for evaluating sexps via
eval-sexp-fu. - Selecting and editing of multiple text elements via
expand-region. - Support for editing files in hex format via
hexl. - Deletion of consecutive horizontal whitespace with a single key
via
hungry-delete. - Support for selecting, copying and opening links using
avyvialink-hint. - Adding of sample text via
lorem-ipsum. - Transient state for moving text via
move-text. - Support for folding of code via
origamiandevil-vimish-fold. - Support for password generation via
password-generator. - Support for improving parenthesis handling via
smartparens. - Automatic whitespace cleanup on save via
spacemacs-whitespace-cleanup. - Support for converting definitions to certain styles via
string-inflection. - Support for generating UUIDs via
uuidgen. - Support for conversion between Emacs regexps and PCRE regexps.
- Support for persistent scratch via
persistent-scratch. - Support for unkillable scratch via
unkillable-scratch. - Support for sorting (press
s) viadired-quick-sort - Support for
evil-easymotionif the editing style isvimorhybrid. - Support for cycling between multi line block styles via
multi-line. - Support for editing strings inplace via
string-edit - Presents undo history as a tree via
undo-tree
11.10. Spacemacs-editing-visual
+spacemacs/spacemacs-editing-visual/README.org
This layer defines a lot of functions used to visually enhance the currently edited line in Spacemacs.
Features:
- Adaptive wrapping
- Hiding of comments
- Highlighting of columns longer than 80 chars
- Highlighting of different indentations
- Automatic highlighting of numbers
- Automatic highlighting of parentheses
- Adaptive cursor shape in terminal, as it would be in GUI
11.11. Spacemacs-evil
+spacemacs/spacemacs-evil/README.org
This layer adds various adjustments to packages to create an evilified experience throughout the entirety of Spacemacs.
Features:
- Add evil tutorial with
evil-tutor - Add escaping under
fdby default withevil-escape - Add occurrences count in mode-line when searching a buffer
- Add support for lisp structure manipulation with
evil-lisp-state - Add safe structural editing of lisp dialects with
evil-cleverparens - Add
evil-exchangeto swap text - Add easy live editing of multiple occurrences with
evil-iedit-state - Add new vim text objects for indentation with
evil-indent-plus - Add operations to align text with
evil-lion - Easy management of comments with
evil-nerd-commenter - Navigation between pairs with
evil-matchit - Advanced navigation on brackets with
evil-unimpaired - Easy increment and decrement of numbers with
evil-number - Support for additional vim movements via
evil-args - Support for surrounding the marked area with a given character via
evil-surround - Evilification of various modes if the editing style is
vimorhybrid - Improves the comment function to be able to also do the inverse operation
- Persistent highlight of searched text with
evil-search-highlight-persist - Display tildes in non-buffer area with
vi-tilde-fringe - Add
evil-collection
11.12. Spacemacs-language
+spacemacs/spacemacs-language/README.org
This layer adds support various language related services to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Show definition of word at point via define-word.
- Integration of google-translate into Emacs via google-translate.
11.13. Spacemacs-layouts
+spacemacs/spacemacs-layouts/README.org
This layer adds support for distinct layouts/workspaces to Spacemacs.
Layouts provide an easy way to group buffers for a project or any arbitrary buffer grouping you wish. Layouts also restrict actions to the buffers in the current layout.
Features:
- Support for distinct layouts via
eyebrowse - Integration with
helmandivyto search for buffers within layouts
11.14. Spacemacs-misc
+spacemacs/spacemacs-misc/README.org
This layer adds some general packages into Spacemacs.
Features:
- Support for jumping to definitions via
dumb-jumporevil-goto-definition. - Support for an easy http request client via
request.
11.15. Spacemacs-modeline
+spacemacs/spacemacs-modeline/README.org
This layer adds various mode-lines to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Display of a vim-powerline like mode-line being able to show various information like
- Current battery status
- All active minor modes displayed as unicode symbols
- The active major mode
- The current branch if the file is in version control
- The current cursor position
- The system clock
- Display of a small system monitor in a separate mode-line.
11.17. Spacemacs-org
+spacemacs/spacemacs-org/README.org
This layer tweaks org-mode to integrate nicely into Spacemacs.
Features:
- Configuration for
flyspellto checkorg-buffersfor typos. - Support for automatically generated Table-Of-Contents via
toc-org. - Support for custom bullet markers via
org-superstar. - Support for a special view mode for org documents via
space-doc.
11.18. Spacemacs-project
+spacemacs/spacemacs-project/README.org
This layer tweaks projectile to integrate nicely into Spacemacs.
Features:
- Setup of
projectilekey bindings, including functions for project search, switching, version control and compilation. - Additional path helper functions, to copy the location of a buffer relative to the project root.
11.19. Spacemacs-purpose
+spacemacs/spacemacs-purpose/README.org
This layer enables window-purpose, which provides an alternative, purpose-based window manager for Emacs. With this layer, your window layout should be robust and shouldn't change too much when opening all sorts of buffers.
Regular popwin is not triggered when window-purpose is enabled. However,
the window-purpose layer provides a purpose-popwin extension, which
brings popwin's behavior to window-purpose and solves that problem.
Features:
- Window layout is more robust and less likely to change unintentionally
- Dedicate window to a purpose
- User-defined purposes
- Extensible window display behavior
- Empty
purpose-mode-map, to avoid conflicts with other key maps - Replicate popwin behavior for purpose-mode - almost no regression in popup behavior from using window-purpose.
- Reuses popwin's settings:
popwin:special-display-config,popwin:popup-window-heightandpopwin:popup-window-width. - Difference from popwin: when several windows are open, popup window is sometimes bigger than with regular popwin in the same situation.
11.20. Spacemacs-visual
+spacemacs/spacemacs-visual/README.org
This layer adds various modes to enhance Spacemacs visual appearance.
Features:
- Automatic colorization of compilation buffers via
ansi-colors. - Support for resuming the last layout when starting Spacemacs via
desktop. - Support for showing a thin vertical line to indicate the fill column
via
fill-column-indicator. - Automatic highlighting of
TODO-tagsin programming and text modes viahl-todo. - Support for temporary windows which close automatically via
popwin. - Support for text zooming via
zoom-frm.
12. Music
12.1. Alda Layer
Alda is a music composition language allowing music to easily be written and edited in a text file.
This layer adds key bindings for alda-mode's functions, which allow Alda code
to be interpreted and played by the running Alda server. It will also start the
Alda server if it is not running.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting for Alda files.
- Play portions of a buffer, or the entire buffer, through a running Alda server.
12.2. Extempore
This layer adds support for the Extempore programming environment.
Features:
- run Extempore (inferior extempore buffer)
- connect to & evaluate code
- eldoc support
12.3. Pianobar
This layer integrates an online music service into Spacemacs.
Features:
- Support for listening to music from within Emacs via Pianobar.
12.4. Spotify
This layer integrates an online music service into Spacemacs.
Features:
- Support for listening to music from within Emacs via Spotify.
12.5. TidalCycles
This layer adds a major mode to control TidalCycles, a programming language for live coding.
Features:
tidal-modeto interact with TidalCycles- Spacemacs friendly key bindings
13. Operating systems
13.1. NixOS
This layer adds tools for better integration of Emacs in NixOS.
Features:
- Nix-mode using nix-mode
- Automatic formatting via nixfmt
- Auto-completion of NixOS Options using company-nixos-options
- Helm Lookup for NixOS Options helm-nixos-options
- WIP support for LSP backend using
rnix-lsp
13.2. OSX
Spacemacs is not just Emacs plus Vim. It can have macOS key bindings too! This layer globally defines common macOS key bindings.
Features:
⌘is set tohyperand⌥is set tometa- In
direduseglsinstead ofls - Fix separator colors of Spaceline mode-line
14. Pair programming
14.1. Floobits
+pair-programming/floobits/README.org
This layer adds support for the peer programming tool floobits to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Loading of floobits configuration files with fixed commands
- Creation of floobits workspaces and populating it with content
- Marking of the current cursor position for all users within the current workspace
- Follow recent changes by other users
15. Programming languages
15.1. Domain-specific (DSLs)
15.1.1. Lisp dialects
- Clojure
This layer adds support for Clojure language using CIDER, providing Clojure REPL management and a full suite of tooling for Clojure development.
Features:
- REPL via CIDER
- Code formatting via CIDER using Cljfmt
- Refactoring via clj-refactor
- Aligning of code forms via clojure-mode
- Debugging with sayid
- Advanced help with helm-cider
- Structuraly safe editing using optional evil-cleverparens
- Linting via clj-kondo (joker and squiggly-clojure also available)
Related layers
The following Spacemacs layers should also be added for a complete experience.
- auto-completion
- syntax-checking (provides flycheck for linter support)
- LSP
Other optional features
- Refactoring via clj-refactor
- Debugging with sayid
References
- Common Lisp
This layer provides support for Common Lisp to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Emacs Lisp
This layer gathers all the configuration related to emacs-lisp. This should always be in your dotfile, it is not recommended to uninstall it.
Features:
- Auto-completion using company
- Linting using flycheck integration
- Linting package file metadata using flycheck-package
- Repl support via
IELM - Support for specific lisp navigation styles via
emacs-lisp-mode - Auto-compile via auto-compile package
- Debugging via edebug
- Ert test runner with overseer
- Nameless package prefix with optional nameless
- Structurally safe editing using optional evil-cleverparens
- Visual feedback when evaluation using eval-sexp-fu
- Provide Emacs Lisp API usage examples using elisp-demos
- Scheme
This layer adds support for Scheme via Geiser. Note that combined usage of racket-mode and geiser has not been tested.
Features:
- Support the Scheme compiler Chicken
- Support for the extension language platform Guile
- Structurally safe editing using optional evil-cleverparens
15.1.2. Markup & configuration
- Asciidoc
- BibTeX
BibTeX and BibLaTeX files are a common way to manage bibliographies. The format was original designed to work with LaTeX files and subsequently has been adopted by other markup formats such as MarkDown and Org mode.
This layer adds support to manipulate BibTeX and BibLaTeX files in Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting for BibTeX and BibLaTeX files.
- Utilities for automatically adding entries from different data sources.
- Support for inserting citations in various other modes.
- Optionally install full fledged ebib reference manager
- CSV
This layer adds tools for better integration of CSV files in Spacemacs.
Features:
- Detecting of fields for various separators
- Aligning of fields
- Traversal of fields
- Killing of fields
- Sorting of rows
- Transposing of rows/columns
- Intelligent yanking of fields
- Dhall
This layer adds support for the Dhall Configuration Language, a non-repetitive alternate to YAML.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting for
.dhallsource files - Automatic buffer reformatting on save (configurable)
- Type error display in side-buffer
Note: You will need a
dhallbinary on yourPATH. Official releases can be found here. - Syntax highlighting for
- Fountain
This layer adds support for the fountain screenwriting format to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Fountain files support via fountain-mode
- Confortable writing layout via olivetti-mode
- Graphviz
This layer adds support for the open-source graph declaration system graphviz to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting for
.dotfiles - Integration of a live-preview of
.dotfiles via graphviz-dot-mode. - Control of the graphviz compiler directly from emacs.
- Support for formatting
.dotfiles automatically.
- Syntax highlighting for
- HTML
This layer adds support for editing HTML and CSS.
Features:
- Editing HTML and CSS file using web-mode
- Support for Sass/Scss and Less files
- Generate HTML and CSS coding using emmet-mode
- Tags navigation on key
%using evil-matchit - Support for editing Slim and Pug templates using slim-mode and pug-mode
- See the effects of typed HTML using impatient-mode
- imenu support for CSS and Sass through counsel-css
- Formatting with web-beautify
- JSON
This layer adds support for JSON files with json-mode
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Auto-completion
- Get the path to a JSON value with json-snatcher
- Navigate JSON hierarchy with json-nagivator
- Formatting with web-beautify or prettier
- Jsonnet
This layer provides support for Jsonnet template provided by jsonnet-mode.
Features:
- syntax highlighting
- buffer formatting
- jump to definition
- buffer evaluation
- LaTeX
This layer adds support for LaTeX files with AucTeX.
Features:
- Auto-build with auctex-latexmk
- Syntax highlighting
- Auto-completion
- Tags navigation on
%with evil-matchit - Labels, references, citations and index entries management with RefTeX
- LaTeX-specific text objects and much more with evil-tex
- Markdown
This layer adds markdown support to Spacemacs.
Features:
- markdown files support via markdown-mode
- mdx file support via markdown-mode
- Fast GitHub-flavored live preview via vmd-mode
- TOC generation via markdown-toc
- Completion of Emojis using company-emoji (still needs a way of showing, either
using the
emojilayer or having a proper font) :clap:
- Plantuml
This layer enables support for plantuml-mode, which provides a major-mode for plantuml. PlantUML is a tool to generate UML diagrams from plain-text.
For help with how to use plantuml, see the plantuml website and the reference guide.
The official file extension supported by this layer is
.pum. and.puml. If you want something else, set it in youruser-configfunction of your~/.spacemacsfile.For example, the following diagram can be defined as follows:
@startuml JAremko->robbyoconnor : I think the docs can benefit from some kind of illustration JAremko<-robbyoconnor : I'm too lazy -- I have actual work to do. I link to the docs. If you can write me a diagram in plantuml, I'll gladly compile and add it. JAremko->robbyoconnor : *gives ths diagram* robbyoconnor<-JAremko : *robbyoconnor adds it and JAremko is happy* ... robbyoconnor->theOtherPerson : And they thinks it's funny? Yup, they definitely finds it funny. Right? @enduml
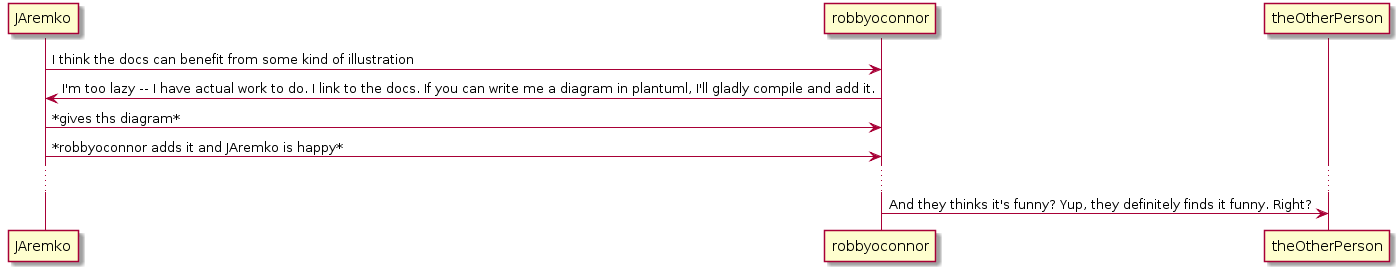
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Diagram preview in various output formats
- Embedding into org documents
- Controlling the
Plantumlcompiler directly from emacs
- ReStructuredText
+lang/restructuredtext/README.org
The layer adds ReStructuredText (ReST) support to Spacemacs and adds some functions to
rst-mode.Note: to add
Sphinxspecific support use the layersphinx.Features:
rstfiles are supported via Emacs built-inrst.el.- Lists are inserted by new functions.
- Directives can be inserted easily.
- snippet support via
yasnippet.
- Semantic Web
This layer adds support for RDF files in N3 and Turtle syntax using ttl-mode and for SPARQL queries using sparql-mode.
SPARQL-mode supports the execution of queries. When first called, you will be prompted for a SPARQL HTTP endpoint in the minibuffer, which defaults to http://localhost:2020/. Once set, it will be used for all subsequent queries in that buffer. Results will be displayed in another buffer in CSV format.
Features:
- Provides an alternative way to search the web using SPARQL queries.
- YAML
This layer provides support for the YAML file format.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Syntax checking via flycheck
- Yang
This layer provides support for the YANG file format.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Syntax checking via flycheck
15.1.3. Scripting
- Autohotkey
Syntax highlighting and Emacs functions for use with AutoHotkey or AutoHotkeyL.
Using a combined implementation of ahk-mode from Xah Lee's
xahk-modeand Robert Widhopf-Fenk'sautohotkey-mode. Updated with the latest ahk and ahkl commands found in the latest revision of SciTE4AutoHotkey.Contributed and maintained by Rich Alesi.
Features:
- Auto-completion
- Documentation Lookup
- Execute Code Snippets
- Correct Indentation and Commenting
- Graphql
This layer adds support for graphql file. It builds around graphql-mode. Please check its site for extra info.
Features:
- Syntax highlight and graphql calls with
graphql-mode - Autocomplete with
comapy-dabbrev - Format buffer with
prettier - Go to definition with
ahs
- Syntax highlight and graphql calls with
- Shell Scripts
+lang/shell-scripts/README.org
This simple layer adds support for shell scripting.
Supported scripting files:
.sh.fish: fish shell
Note: For Windows scripting see the layer
windows-scriptsFeatures:
- Auto-completion using company-shell
Shscripts linting using shellcheckShscripts style checking using bashate- Support for the Language Server Protocol (experimental)
- Automatic formatting via shfmt
- Vimscript language
This layer adds support for vimscript and pentadactyl config files.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Auto-completion (with LSP)
- Syntax-checking (with LSP)
- Windows Scripting
+lang/windows-scripts/README.org
This simple layer adds support for the Powershell scripting language as well as support for batch files.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting of powershell
.ps1files via powershell.el - Syntax highlighting of batch
.batfiles via bat-mode - Auto-completion, code-navigation and refactoring capabilities of batch files via bmx-mode
- Syntax highlighting of powershell
15.1.4. Coq
This layer adds support for the Coq proof assistant (adapted from spacemacs-coq) to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Syntax-checking
- Auto-completion (requires the auto-completion layer to be installed)
- Debugging of mathematical proofs from within Emacs using a special proof layout
- Replacement of certain constants with the correct mathematical signs
- Inserting of certain preconfigured proof elements
15.1.5. Elasticsearch
+tools/elasticsearch/README.org
This layer adds Elasticsearch query and monitoring support to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Autocompletion for Elasticsearch Query DSL
- Support for Org-Babel
- Support for an Elasticsearch Command Center to monitor a cluster
15.1.6. ESS (R)
This layer adds support for statistical programming languages to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Auto-completion
- Syntax-checking via lintr
- Additional data viewer for R via ess-R-data-view
- Support for Org-Babel
- Showing of inline help for
Rconstructs - Repl support via
R terminal - Support for
S,SASandR - Much more via the ESS Project
15.1.7. Extra Languages
This layer adds a number of packages for less common languages and major modes.
Features:
- Support for:
- Arch Linux PKGBUILDs
- Arduino
- Android Logcat (not associated with any file types by default)
- Gemtext
- Gentoo ebuilds
- Hoon
- MATLAB
- QML
- OpenScad
- Stan
- Thrift
- Vala
- Wolfram Language / Mathematica
15.1.8. Faust
This layer adds support for the faust language to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Auto-completion
15.1.9. GPU
This layer adds support for GPU related languages like CUDA, OpenCL and various Shader formats to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting for
.cl(OpenCL).cu(CUDA).cuh(CUDA).fsh(Shaders).vsh(Shaders).glsl(Shaders).vert(Shaders).frag(Shaders).comp(Shaders).geom(Shaders).tesc(Shaders).tese(Shaders)
- Simple auto-completion via company-glsl for
.vert(Shaders).geom(Shaders).tesc(Shaders).tese(Shaders).frag(Shaders).comp(Shaders)
15.1.10. Kivy
This layer adds support for Kivy, cross-platform GUI framework for Python.
Features:
- Syntax Highlighting
15.1.11. Mercury
This layer adds support for the Mercury language.
Features:
- Indentation.
- Syntax highlighting.
- Compiling and running.
15.1.12. Octave
This layer adds support for GNU Octave files to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting for
.mfiles via octave-mode. - REPL support
- Support for directly running
Octavescripts from Emacs. - Integration with
Octavesdocumentation search function.
15.1.13. Prolog
This layer adds support for Prolog using the bundled Prolog mode for Emacs. In addition it also adds ediprolog support for better interaction with SWI-Prolog.
Features:
- Designed for SWI-Prolog as a default, but can be used with other Prologs that Prolog mode supports.
- Interactive consulting and compiling.
- Auto-formatting.
- Apropos and help lookup.
15.1.14. Solidity Layer
A layer to support Solidity development in Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Syntax checking
- Gas estimation
15.1.15. SQL
This layer adds support for a wide range of SQL dialects to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting for the following SQL dialects
- ANSI
- DB2
- Informix
- Ingres
- Interbase
- Linter
- Microsoft
- MySQL
- Oracle
- Postgres
- Solid
- SQLite
- Sybase
- Vertica
- Syntax-checking via sqlint for ANSI SQL.
- Format code with
sqlfmt - Snippet insertion for the more general SQL constructs.
- REPL support via
SQLibuffer. - Automatic capitalization of keywords.
- LSP support via sqls.
15.2. Frameworks
15.2.1. Django
This layer adds support for the Python web framework Django to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Test execution directly from emacs
- Starting/stopping of the Django test server
- Starting of an interactive Python shell in the current project for debugging
- Fixed commands to open various Django specific settings files
- Automatic deployment with Fabric directly from emacs
- Control of South database migration tool
15.2.2. Emberjs
+frameworks/emberjs/README.org
This enables helpers for working with Ember.js projects.
This also includes ember-yasnippets. See the README for ember-yansippets for the snippet keys.
To use this, you need to add add a .dir-locals.el file with the following in the root of your ember project:
((nil . ((mode . ember))))
If you do not wish to do the following, you may also just do M-x ember-mode, however it will make things easier.
Additionally, temporary backup, autosave, and lockfiles interfere with broccoli watcher, so they need to either be moved out of the way or disabled.
Add the following to your dotspacemacs/user-config:
(setq backup-directory-alist `((".*" . ,temporary-file-directory))) (setq auto-save-file-name-transforms `((".*" ,temporary-file-directory t))) (setq create-lockfiles nil)
Features:
- Ability to easily switch between various files
- Key bindings for generators and also easily revert generator actions
- Ability to build, start server, and run tests
15.2.3. Phoenix
+frameworks/phoenix/README.org
This layer adds key bindings for Alchemist's already built in phoenix mode.
Features:
- Key bindings for navigation to files
15.2.4. React
ES6 and JSX ready configuration layer for React
It will automatically recognize .jsx files and files with react imported.
Features:
- on-the-fly syntax checking
- proper syntax highlight and indentation with jsx
- backend support for autocompletion as in rjsx-mode
- jsfmt automatic formatting
- js2-refactor
- js-doc
15.2.5. Ruby on Rails
+frameworks/ruby-on-rails/README.org
This layer aims at providing support for the Ruby on Rails framework.
Features:
- Quick file navigation with with projectile-rails
- Run server
- Run generators
- Rake runner
- Interactive Rails console
15.2.6. Svelte
Layer for Svelte, for working with .svelte files.
Note: This layer creates a derived mode called svelte-mode on the fly out of
web-mode to handle svelte files. It will conflict with the svelte-mode package, make sure
you don't use that package together with this layer.
Features:
- Wholesome features from
web-mode, especially on template part - Better performance
- On-the-fly syntax checking with
eslint - Proper syntax highlight and indentation with
svelte-mode - Two options for backend support for autocompletion and code analysis:
lspanddumb - Code autocompletion with
company-mode - Formatting code with
prettierlayer evil-matchit%to jump between open and close tagsemmet-modeandyasnippetfor code expanding with theTABkey
15.2.7. Vue
Layer for Vue, for working with .vue files.
Note: This layer creates a derived mode called vue-mode on the fly out of
web-mode to handle vue files. It will conflict with the vue-mode package, make sure
you don't use that package together with this layer.
Features:
- Wholesome features from
web-mode, especially on template part - Better performance
- On-the-fly syntax checking with
eslint - Proper syntax highlight and indentation with
vue-mode - Two options for backend support for autocompletion and code analysis:
lspanddumb - Code autocompletion with
company-mode - Formatting code with
prettierlayer evil-matchit%to jump between open and close tagsemmet-modeandyasnippetfor code expanding with theTABkey
15.3. General-purpose
15.3.1. Imperative
- Asm
This layer adds support for Assembly code. The built-in major mode for editing assembly code in Emacs is
asm-mode.The layer also adds
nasm-modefor NASM-specific syntax. Althoughnasm-modeis intended for NASM, it actually works well with other variants of Assembly in general, and provides Imenu integration so you can jump around withSPC s j.Features:
- Improved syntax highlighting.
- Automatic indentation.
- Auto-completion for symbol in opened buffers.
- Look up documentation for current instruction at cursor.
- Imenu integration.
- Forth
This layer adds basic support for the Forth family of languages to spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Showing meaning of objects in context of the current
Forthsession. - Eval of entire files or regions in current
Forthsession. - Passing interactive commands to current
Forthsession.
15.3.2. Multi-paradigm
- JavaScript dialects
- CoffeeScript
This layer adds support for the CoffeeScript language using coffee-mode.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Auto-completion with
auto-completionlayer - Syntax checking and linting with
syntax-checkinglayer Org-Babelintegration- REPL support
- JavaScript
This layer adds support for the JavaScript language using js2-mode.
Features:
- Multiple backends support: Tern and LSP
- Smart code folding
- Refactoring: done using js2-refactor.
- Auto-completion and documentation
- Browser based REPL available via skewer-mode and livid-mode
- Server based REPL with nodejs-repl
- Formatting with web-beautify or prettier
- Interactive debugger using dap-mode
- Display Flow & Typescript type information
- Purescript
This layer provides basic Purescript editing support for spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting through purescript-mode
- Automatic insert of imports through psc-ide-emacs
- REPL through psci
- Syntax checking through flycheck
- Autocompletion through company
- TypeScript
This layer adds support for TypeScript and TSX editing.
Features:
- Multiple backends support: Tide and LSP
- Eldoc-mode
- Documentation at point
- Auto complete
- Flycheck with either eslint or tslint
- Jump to definition, Jump to type definition
- Find occurrences (Imenu-mode)
- Rename symbol
- tsx mode
- formatting
- TypeScript playground integration
- CoffeeScript
- C#
This layer adds support for the C# language using the omnisharp-roslyn language server with either the omnisharp-emacs or the lsp-mode packages.
Features:
- Syntax checking with flycheck (when
syntax-checkinglayer is used) - Support for auto-completion (when
auto-completionlayer is used) - Refactoring
- Navigation to cross-references
- Inspecting types in metadata
- Syntax checking with flycheck (when
- C/C++
This layer adds configuration for C/C++ language.
Features:
- Multiple backends support:
- LSP with either
clangdor ccls - rtags (gtags)
- emacs-ycmd
- LSP with either
- Support for debuggers realgud and dap (with LSP backend)
- Support syntax checking via flycheck (
syntax-checkinglayer required) - Auto-completion via company (
auto-completionlayer required) - Support code reformatting with clang-format.
- Support for disassembly of code with disaster.
- Doxygen code documentation comment generation (using gendoxy).
semanticlayer integration:- Function or variable definition at the bottom
- Support common refactoring with semantic-refactor. See srefactor-demos for demonstration of refactoring features.
cscopelayer integration:- code navigation
- Multiple backends support:
- Crystal
This layer provides support for the Crystal language.
Features:
- Format on save
- Integration of play.crystal-lang.org using play-crystal.el
- Syntax checking
- Auto completion
- Test execution (
crystal spec) crystal toolintegration- Interactive REPL (inf-crystal.el and icr)
- Static code analysis using ameba
- D language
This simple layer adds support for the D language to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Auto completion via
company - Syntax checking via
flycheck
- Dart
This layer adds support for Dart language, and could be optionally used for Flutter development as well.
Features:
- Syntax Highlight
- Error checking with
flycheck - Go to Definition
- Dart Analyzer integration
- Key bindings
- Elixir
This layer adds support for Elixir.
Alchemist brings the Elixir tooling to Emacs and comes with a bunch of features. Lsp-mode brings IDE like features following Language Server Protocol, through elixir-ls
As Alchemist is no longer maintained, elixir-ls is a preferred solution, even though it has less features at the moment.
Features:
- Powerful IEx integration
- Mix integration
- Compile & Execution of Elixir code
- Inline code evaluation
- Documentation lookup
- Definition lookup
- Smart code completion
- Elixir project management
- Integration with company-mode
- Flycheck support for credo
- Flycheck support for test results
- Interactive debugger using dap-mode
- Erlang
This layer adds support for Erlang.
Enabling Lsp-mode brings IDE like features following
Language Server Protocol, through erlanglsFeatures:
- Syntax highlighting
- Syntax checking via
Flycheckintegration - Auto-completion via
Companyintegration - Code Completion
- Go To Definition
- Go To Implementation for OTP Behaviours
- Signature Suggestions
- Compiler Diagnostics
- Dialyzer Diagnostics
- Elvis Diagnostics
- Edoc
- Navigation for Included Files
- Find/Peek References
- Outline
- Workspace Symbols
- Code Folding
- Interactive debugger using dap-mode
- F#
This layer adds support for F# language using fsharpbinding and fsharp-mode.
Features:
- Auto-completion
- Syntax-checking
- Syntax highlighting
- REPL
- Factor Layer
A spacemacs layer for Factor language support.
Features:
- Syntax Highlighting
- Factor REPL integration
- Auto-Completion in REPL
- Scaffolding support
- Refactoring support
- Running graphical Listeners
- Reloading emacs-lisp portion of FUEL
- Go
This layer adds extensive support for the Go programming language.
Features:
- Run gofmt / goimports on file save (see Autoformat)
- Auto-completion
- Source analysis using go-guru (see Guru)
- Refactoring with godoctor
- Edit struct field tags with gomodifytags
- Syntax checking with flycheck's built-in checkers or golangci-lint (see Linting)
- Test generation via go-gen-test (see Tests)
- Coverage profile visualization (see Coverage)
- List packages faster with gopkgs
- Fill a structure with default values using the fillstruct
- Gopls backend support (see LSP backend)
- Interactive debugger with LSP using dap-mode
- Groovy
This layer supports Groovy development in Spacemacs.
Features:
- Auto-completion
- Syntax-checking
- Auto-generate imports with groovy-imports
- Groovy REPL integration
- Syntax highlighting
- Hy
This layer adds support for the Hy language based on Python.
Features:
- syntax-highlighting
- Auto-completion
- Code Navigation
- Python test runners (see python layer)
- Virtual Environment using pyvenv and pyenv
- Org Babel support
- Java
This layer adds support for the Java language.
Features:
- JR Concurrent Programming Language
This layer adds syntax highlighting for the JR Concurrent Programming Language. JR is the implementation of the SR language for Java.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Julia
This layer adds support for Julia to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Repl support
- Linting
- Completion
- Jump-to-definition
- Documentation on hover
- Kotlin
This layer adds support for Kotlin to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Auto-completion
- Syntax-checking with ktlint and flycheck-kotlin
- Navigation with
ggtags
- Lua
This layer adds support for editing Lua.
Features:
- Nim
This layer adds support for the multi-paradigm language
Nim.Features:
- Auto-completion
- Syntax-checking
- Jump to definition.
- Ocaml
This is a very basic layer for editing ocaml files.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting (major-mode) via tuareg-mode
- Error reporting, completion and type display via merlin
- auto-completion with company mode via merlin
- syntax-checking via flycheck-ocaml (or alternatively merlin)
dunefile syntax highlighting and template insertion via dune-mode- Automatic formatting via ocamlformat
- Pact
This layer adds support for the Pact Smart Contract Language.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting for
.pactsource files - Easy interaction with an embedded Pact REPL
- Flycheck integration
Note: You will need a
pactbinary on yourPATHfor REPL features to function. - Syntax highlighting for
- Perl5
This layer adds support for the Perl5 language.
Features:
- PHP
This layer adds PHP language support to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Edit PHP files using php-mode
- Edit Drupal files
- Complete and jump to define with company-php
- Run tests with PHPUnit
- Reformat code with PHP CBF
- Debug your programs with XDebug (via geben or dap-mode)
- Refactor source files with help of phpactor.el
- Support for the Language Server Protocol (experimental)
The
gtagslayer is recommended to benefit from bettereldocandhelm-gtags. - Python
This layer adds support for the Python language.
Features:
- Support for the following backends:
- anaconda (default),
- Language Server Protocol (experimental - 2 implementations),
- python-lsp-server
- Microsoft pyright language server
- Auto-completion
- Code Navigation
- Documentation Lookup using anaconda-mode and pylookup
- Test Runners using nose.el or pytest
- Virtual Environment using pyvenv and pyenv as well as pipenv and poetry
- semantic mode is enabled
- PEP8 compliant formatting via YAPF or black
- PEP8 checks with flake8 or pylint
- Suppression of unused import with autoflake
- Use the
%key to jump between blocks with evil-matchit - Sort imports with isort
- Fix a missing import statement with importmagic
- Pip package manager with pippel
- Interactive debugger using dap-mode
- Support for ipython notebook and MATLAB-like cells using using code-cells
- Support for the following backends:
- Racket
Adds support for the Racket programming language.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting with
racket-mode - Test runner
- Interactive REPL
- Code navigation with
gtags - Structurally safe editing using optional evil-cleverparens
- Syntax highlighting with
- Raku
This layer provides an environment for the Raku Programming Language that was previously known as Perl 6.
Features:
- Jump to definition & Code completion via ctags-universal
- Syntax checking via flycheck-raku and
raku -c - Syntax highlighting & Syntax indentation via raku-mode
META6.jsonhighlighting via json-mode- Provides Evil text objects for:
- double-angle-brackets
- corner-brackets
- single-quotation-marks
- double-quotation-marks
- ReasonML
Spacemacs layer for ReasonML, based around reason-mode.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting / indentation
- Autocomplete (via
merlin) - Lint / error display (via
merlin, andflycheckifsyntax-checkinglayer is enabled) - REPL via
rtop - Auto-formatting (via
refmt)
- Ruby
This layer provides support for the Ruby programming language.
Features:
- Version manager (rbenv, rvm or chruby)
- Integration with bundler
- Test runner (ruby-test and rspec)
- Rake runner
- Linter (rubocop)
- Formatter (prettier)
- Interactive REPL and code navigation (robe)
- Interactive debugger using dap-mode
- Rust
This layer supports Rust development in Spacemacs.
Features:
- Auto-completion and navigation support through lsp-mode
- Interactive debugger using dap-mode
- Support for the Rust package manager Cargo
- Support for Rusty Object Notation (RON)
- Scala
This layer adds support for the Scala language to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Support for language backend using LSP and Metals
- Debugging support via
dap - Auto-completion
- Treeview support for viewing project structure and triggering compilation
- Syntax-checking
- Refactoring
- Incremental compilation
- Style linting
- Optional GGTags search
- SML
Adds support for the SML programming language to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Integration of the
SML Replinto Emacs - Basic completion of SML forms via
sml-electric-space - Basic buffer formatting with
smlfmt
- Swift
This layer adds support for Apple's Swift programming language, used as a general purpose scripting language.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting with swift-mode
- Indentation
- Code navigation using
imenu(built-in) - Automatic syntax checking with
flycheck(available with thesyntax-checkinglayer)
- Zig
This layer adds support for the zig programming language https://ziglang.org/
Features:
- Syntax Highlighting
- LSP support via
zls(see LSP)
15.3.3. Purely functional
- Agda
This layer adds support for the Agda programming language.
Features:
- Faces redefined to correctly play with themes.
- Spacemacs bindings to Agda's interactive tools.
This layer is in construction, it needs your contributions and bug reports.
- Elm
This layer adds support for Elm.
It relies on elm-mode and flycheck-elm.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting.
- Intelligent indentation
- Auto-completion integration for company (default) or auto-complete modes
- Syntax checking support using flycheck
- Integration with elm-make
- Integration with elm-repl
- Integration with elm-reactor
- Integration with elm-package
- Gleam
This layers adds support for Gleam. It relies on the official gleam-mode package and tree-sitter-indent.
Features:
- Gleam language server integration
- Formatting (
gleam format) - Execution (
gleam build,gleam run,gleam test)
- Haskell
This layer adds support for the Haskell language.
Features:
- syntax highlighting for haskell source, cabal files, C– source
- auto-completion and syntax-checking with one of the selected backends (
danteorlsp).
- Idris
This layer adds support for the Idris language to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Syntax checking via
flycheck - Integration of the
IdrisREPL - Integration of the
Idrisbuild system
15.4. Utilities
15.4.1. Conda Layer
This layer adds support for the Anaconda python environment for numerical computations to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Controlling
AnacondaorMinicondaenvironments directly from emacs with conda.el
15.4.2. Dotnet
This layer adds support for the dotnet cli package.
Features:
- dotnet project operations
15.4.3. IPython Notebook
+tools/ipython-notebook/README.org
This layer adds support for the package emacs-ipython-notebook.
Do not hesitate to check the original package README here. Also the wiki has lots of informative stuff.
Features:
- Key bindings available through transient-state or leader key
- Lazy-loading
- Auto-completion
15.4.4. Protocol Buffers
Highlighting and syntax checking for Protocol Buffer files.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Syntax checking using Flycheck (
protoccompiler must be available) - Correct indentation and commenting
- Quickly browse file contents using imenu (default key binding
SPC b t).
15.4.5. Sailfish OS developer
+tools/sailfish-developer/README.org
This layer adds support of sailfish-os development packages.
Features:
- sailfish-scratchbox: handy sb2 interaction.
16. Readers
16.1. Dash
This layer integrates offline API browsers into Emacs. It provides one for macOS, Linux and Windows.
Features:
16.2. Deft
This layer adds a search driven note taking system into Spacemacs.
Features:
- Browsing and creating notes with a powerful search function via Deft.
- Integration of
org-modeas note editor. - Configurable list of extensions to recognize as notes.
- Zettelkasten system with zetteldeft
16.3. Djvu
This layer adds support for reading djvu files with spacemacs.
Because of some difficulties, the layer does not lazy load the djvu.el and
djvu3.el packages.
Features:
This layer provides a full featured djvu editor by implementing the djvu.el package along with the djvu3 extension (a newer alternative to djvu2.el).
- flexible annotation editing and rendering, covering most (but not all) of djvused annotation definitions
- fast navigation with imenu
- fast search with djvu-occur
- remember last view with djvu-restore
- dark mode
16.4. Elfeed
This layer integrates a web feed reader into spacemacs.
Features:
- Support for reading RSS and Atom feeds directly within emacs via Elfeed.
- Support for managing feeds via org files supplied by elfeed-org.
- Support for displaying feed database content in the browser via web interface.
16.5. Epub
This layer provides support for reading EPUB-formatted eBooks in Spacemacs using the excellent nov.el package.
Features:
- Basic navigation (jump to TOC, previous/next chapter)
- Remembering and restoring the last read position
- Jump to next chapter when scrolling beyond end
- Renders EPUB2 (.ncx) and EPUB3 (<nav>) TOCs
- Hyperlinks to internal and external targets
- Supports textual and image documents
- View source of document files
- Metadata display
- Image rescaling
16.6. PDF
This layer enables support for PDF with the pdf-tools package.
According to the official repository:
"PDF Tools is, among other things, a replacement of DocView for PDF files. The key difference is, that pages are not pre-rendered by e.g. ghostscript and stored in the file-system, but rather created on-demand and stored in memory."
Features:
- Searching and slicing with
occur. - Show document headings in outline buffer.
- Manipulate annotations.
- Fit PDF to screen.
16.7. Speed Reading
+readers/speed-reading/README.org
A speed reading mode for Emacs.
Features:
- Support for
speed-readingof arbitrary texts
18. Source control
18.1. Git
+source-control/git/README.org
This layers adds extensive support for git to Spacemacs.
Features:
- git repository management the indispensable magit package
- forge add-on for magit.
- git-flow add-on for magit.
- quick in buffer history browsing with git-timemachine.
- quick in buffer last commit message per line with git-messenger
- colorize buffer line by age of commit with smeargle
- git grep with helm-git-grep
- org integration with magit via orgit
New to Magit? Checkout the official intro and Practicalli Spacemacs guide to configuring and using the Git and version control layers.
18.2. Perforce
+source-control/perforce/README.org
This layer integrates Perforce SCM system into Spacemacs.
Features:
- Support for running Perforce (p4) SCM commands directly from Emacs.
18.3. Version-Control
+source-control/version-control/README.org
This layers adds general configuration for Emacs VC. It should work with all VC backends such as Git, Mercurial, Bazaar, SVN, etc…
Features:
- highlights uncommitted changes in the fringe or margin with diff-hl or git-gutter
- adds vcs transient-state
SPC g.to allow quick navigation and modification of buffer hunks.
19. Spacemacs
19.1. Distributions
19.1.1. Spacemacs distribution
+distributions/spacemacs/README.org
This is the default distribution for Spacemacs.
Features:
- Easy access to the Spacemacs experience by adding below auxiliary layers
to the base distribution.
- helm
- treemacs
- spacemacs-completion
- spacemacs-layouts
- spacemacs-editing
- spacemacs-editing-visual
- spacemacs-evil
- spacemacs-language
- spacemacs-misc
- spacemacs-modeline
- spacemacs-navigation
- spacemacs-org
- spacemacs-purpose
- spacemacs-visual
19.1.2. Spacemacs-base distribution
+distributions/spacemacs-base/README.org
This is the base distribution for Spacemacs.
Features:
- Minimalistic approach to Spacemacs, contains only the core packages. Good starting point to make something completely new. This distribution should not be used for a new standalone Spacemacs installation except you have very good reasons to.
19.1.3. Spacemacs-bootstrap distribution
+distributions/spacemacs-bootstrap/README.org
This layer loads the necessary packages for spacemacs to start-up.
Features:
- Loads
evilkey bindings and macros for auto-evilification of maps - Loads
holyandhybridmodes - Loads the official Spacemacs theme
- Loads
use-packagewhich is used to load other packages more easily - Loads
hydrawhich is used to create transient modes - Loads
which-keywhich is used to show key bindings in other modes - Loads
asyncwhich is used to run background processes - Loads
bind-mapandbind-keywhich are used to realize various Spacemacs specific key binding commands
20. Tagging
20.1. Cscope
21. Themes
21.1. Colors
This layer colors your life by enhancing the existing coloration of identifiers as well as providing you with a more colorful process indicator.
Features:
- Colorize all identifiers (Christmas tree mode :-)) with mostly unique colors, and the ability to choose saturation and lightness with rainbow-identifiers.
- Colorize only identifiers recognized as variables with color-identifiers.
- Colorize strings representing colors with the color they represent as background with rainbow-mode.
- Display a Nyan cat progress bar in the mode-line with nyan-mode.
21.2. Themes Megapack
+themes/themes-megapack/README.org
This layer installs around 100 themes for Emacs.
Features:
- Have access to all included themes in this theme gallery from Rob Merrell.
- Easily try a theme by invoking helm-themes with:
SPC T s.
21.3. Theming
This layer allows for a simple way of modifying themes.
Features:
- Modify themes from your
.spacemacs. - Tweak face attributes and other aspects of themes.
- Includes three additional layer variables for tweaking headings.
22. Tools
22.1. Ansible
This layer adds support for editing Ansible configuration files in Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting for Ansible-flavored YAML and Jinja2 templates.
- Auto-completion via
company-ansible. - Integration of
ansible-vaultinto emacs for automatic encryption/decryption of files.
22.2. Apache
This layer adds support for configuring the Apache web server.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting of apache configuration files via apache-mode.
- Syntax-aware indentation
22.3. Bm
bm provides visible, buffer local, bookmarks and the ability to jump forward and backward to the next bookmark.
Features:
- Auto remove bookmark after jump to it by
bm-nextorbm-previous - Cycle through bookmarks in all open buffers in LIFO order
- Toggle bookmarks. Jump to next/previous bookmark.
- Setting bookmarks based on a regexp. (Useful when searching logfiles.)
- Mouse navigation.
- Annotate bookmarks.
- Different wrapping modes.
- Different bookmarks styles, line-only, fringe-only or both.
- Persistent bookmarks (buffer local), also in non-file buffers (info) and indirect buffers.
- List bookmarks (in all buffers) in a separate buffer.
- Cycle through bookmarks in all open buffers.
22.4. CFEngine
This layer adds support for CFEngine policies to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting (CFEngine DSL, Mustache)
- On the fly syntax checking via
flycheckintegration. - Auto completion via
companyintegration. - Execution of
cfengine3SRCblocks inorg-modeviaob-cfengine3package.
22.5. Chrome
This layer provides some integration with the Google Chrome browser.
Features:
- Edit text boxes with Emacs using edit-server
- Write markdown in Emacs and realtime show in chrome using flymd
- gmail message mode uses standard markdown key bindings
22.6. CMake
This layer adds support CMake scripts.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Auto-completion
- Support for CMake configure/build (with limited support for other build systems) and
automatic generation of
compile_commands.json(compile flags). - Run selected test using
Helminterface viahelm-ctest. - Extraction of compile parameters from
compile_commands.jsonwith cmake-ide
22.7. Command-log
This layer adds handy commands for demonstrating Spacemacs.
Features:
- Support for logging all entered keys and triggered commands in a designated buffer via command-log-mode.
- Experimental support for logging the last command directly in the mode line via keycast.
- Provides the best way to demonstrate the connection between keystrokes and commands in Emacs.
- Provides an easy way to create command logs for training classes.
22.8. DAP
Experimental integrated visual debugger using Debug Adapter Protocol.
Debug Adapter Protocol is a wire protocol for communication between client and Debug Server. It similar to the LSP but providers integration with debug server.
Features:
Fully featured IDE-like debugger providing:
- Launch/Attach
- Breakpoints
- Exceptions
- Pause & Continue
- Step In/Out/Over
- Callstacks
- Threads
- Multiple simultaneous debug sessions
- Evaluating statements
- Debug/Run configurations
- Debug REPL
22.9. Debug
This layer adds interactive debuggers for multiple languages using realgud.
Features:
- Modern rewrite of the Emacs GUD debugger family
- Visual interface including breakpoint and line indicators
- Advanced features like stack frame navigation and mouse support
- Extensible framework for adding your own external debuggers
22.10. Docker
This layer integrates basic container management into Spacemacs.
Features:
22.11. Eglot
This layer adds support for basic language server protocol packages speaking language server protocol using eglot.
Features:
- Provide LSP support using eglot.
22.12. Eww
Ewww.. So ergonomic!
Features:
- Adds evil key bindings support to eww-mode (including eww-buffers/bookmarks/history-mode)
- Adds spacemacs functionality to eww-mode
- Adds ability to easily navigate eww buffers
22.13. EXWM
+window-management/exwm/README.org
Thanks to @ch11ng and his EXWM project we can now use Emacs as our window manager, that means that you can spawn a Browser Window, or your music player, or anything.
Features:
- Support for using Emacs as window manager
22.14. Fasd
This layer integrates the fasd command line tool into Spacemacs.
Features:
- Adds easy shortcuts to reference recent files and directories.
- Provides
fasdwith recent open file lists from Emacs. - Allows to filter
fasdresults withhelmorivy.
22.15. Finance
This layer integrates a full fledged accounting system into Spacemacs.
Features:
- Support for maintaining a double-entry accounting system run by text files via ledger-mode.
- Display of finance reports directly within Emacs.
- Integration of Emacs calculator mode for editing post amounts.
- Support for easy account reconciliation via
Ledger-Reconcile. - Extended support for
evilstyle editing with evil-ledger.
22.16. Geolocation
This layer offers location sensitive adjustments to Emacs.
Features:
- Supports the following adjustments:
- Automatic switching between light (day) and dark (night) themes via theme-changer
- Local weather forecast via sunshine
- Integration with macOS's CoreLocation service via osx-location
- Manual location setting via variables in your dotfile
22.18. Import-js
This layer adds support for import-js
Features:
- Import Javascript/Typescript modules to buffer
- Import missing modules and remove unused one
- Go to module location
22.19. Kubernetes
This layer provides the kubernetes-el package, a magit-style interface to the Kubernetes command-line client.
Features:
- Live-updating lists of kubernetes resources
- Viewing and deleting pods, configmaps and secrets
- Switching contexts and namespaces.
- Showing logs and exec'ing into containers
- Describing pods
- Tramp support for pods
- Evil bindings
22.20. LSP
This layer adds support for basic language server protocol packages speaking language server protocol.
Different language servers may support the language server protocol to varying degrees
and they may also provide extensions; check the language server's website for
details.
M-x lsp-describe-session in a LSP buffer to list capabilities of the server.
Warning:
This layers main purpose is to turn Spacemacs into an IDE it will therefore also
load the syntax-checking and auto-completion layers, this may activate additional packages
like flycheck and company in your buffer.
So if you want to use this layer but only part of the IDE features expect to do some manual configuring in your dotfile.
Features:
- Cross references (definitions, references, document symbol, workspace symbol search and others)
- Workspace-wide symbol rename
- Symbol highlighting
- Flycheck
- Completion with
LSP - Signature help with
eldoc - Symbol documentation in a child frame (
lsp-ui-doc) - Navigation using
imenu - Consistent core key bindings in LSP modes
- Code folding (
lsp-origami) - Sonarlint integration (
lsp-sonarlint)
22.21. Meson
This layer adds support Meson scripts.
Features:
- Support for meson build scripts through meson-mode.
- Syntax highlighting.
22.22. Nginx
This layer adds support for configuring nginx a powerful alternative for the Apache web server.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting of nginx configuration files via nginx-mode.
- Syntax-aware indentation
22.23. Node
This layer introduces packages that target Node.js. Currently this layer should not be used directly, as it will be used by other layers.
Features:
- Integration of packages necessary to execute node.js modules from other layers.
22.24. Pandoc
This layer adds support for Pandoc.
Pandoc is a universal document converter. It makes it easy to e.g. convert a Markdown file to org mode or vice versa. It can also export your text to PDF or DOCX.
Features:
- Mode independent document conversions via
global pandoc menu Org-exportintegration via ox-pandoc
22.25. Pass
This layer adds integration with pass, the unix password manager.
You must have pass installed and available in your path for this layer to
function properly.
Features:
- Use Spacemacs as your password manager
- Support for OTP via (password-store-otp)
- Use password-store as an Emacs auth source (auth-source-pass) See its info page for more details on using it.
22.26. Prettier
22.27. Prodigy
This layer adds support for the prodigy package to manage external services from within Emacs, check the package's documentation for more details.
It is recommended to put your prodigy services in the dotspacemacs/user-config
part of your ~/.spacemacs file.
Features:
- Managing of pre-declared services from within Emacs
- Showing of process output in special buffers
- Filtering of processes for tags or names
22.28. Puppet
This layer provides support for the Puppet DSL to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting via puppet-mode
- Syntax-checking via puppet-lint
- Navigation commands to jump between blocks
- Applying the content of the current manifest directly from Emacs
22.29. Ranger
This layer brings Ranger features to spacemacs from the ranger package.
To use this configuration layer, add it to your ~/.spacemacs. You will need to
add ranger to the existing dotspacemacs-configuration-layers list in this
file.
To use ranger/deer by default set ranger-override-dired to ranger/deer like
shown in the example below (setting this via customize as explained by the
original ranger installation instructions will not work). To default with
preview enabled when entering ranger set ranger-show-preview to t. The following
example code shows how you can set both variables at once via the
dotspacemacs-configuration-layers of your dotfiles as follows:
(setq-default dotspacemacs-configuration-layers '(ranger :variables ranger-override-dired 'ranger ranger-show-preview t))
Features:
- use ranger to display dired with ranger like preview and stacked parent windows.
22.30. Rebox
This layer adds support for rebox2 package which is a minor-mode allowing to easily add ASCII text boxes to a buffer.
A nice video demonstration by the package author can be found here.
Features:
- Auto-wrap correctly in comments,
- Auto-fill correctly in comments,
- Boxes auto-adapt as text is inserted or deleted,
S-RETto continue a comment on the next line,- Kill/yank within the box,
- Apparently works well with ancient
filladpt-mode(see authors video).
22.31. Restclient
This layer provides a REPL-like interface for http requests.
Features:
- REPL for http requests via restclient
- Alternative
orgintegration via ob-http
22.32. Saltstack
This layer provides syntax highlighting for Saltstack files.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Display of salt documentation
22.33. Shell
This layer configures the various shells available in Emacs.
Features:
- Shell integration
- Running external terminal emulator in current/project directory
22.34. Sphinx
The layer adds support for the documentation generation system Sphinx to
the restructuredtext layer.
Features:
- Support for
Sphinxproject compilation - Support for opening
Sphinxproject target - Support for opening
Sphinxconfig file
22.35. Systemd
This layer adds support for editing systemd configuration files in Spacemacs.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Auto completion
- Syntax checking via
systemd-analyze - Viewing systemd system and user unit via journalctl-mode
22.36. Tern
This layer adds support for tern stand-alone code-analysis engine for JavaScript.
Features:
- TODO: list the feature of tern supported by tern package
22.37. Terraform
This layer provides basic support for Terraform .tf files.
Features:
- Basic syntax highlighting via terraform-mode
- Auto formatting on save via
terraform fmt - LSP support for terraform-lsp via
terraform-backend
22.38. Tide Layer
This layer installs tide package which allows communication with
standalone typescript server tsserver for JavaScript/TypeScript development.
Features:
- First class support from
tsserverjust likevscode: speed and accuracy - Linter
- Refactor
- Go to definition
- Find references
22.39. Tmux
This layer adds basic tmux key bindings to Spacemacs.
Features:
- Calling of
tmuxnavigation commands directly from Emacs via evil-tmux-navigator.
22.40. Translate Layer
This layer is designed for Paragraph-oriented minor mode for side-by-side document translation workflow.
Features:
- Paragraph-oriented side-by-side document translation workflow
- Integrate word/paragraph online translation
22.41. Transmission
+tools/transmission/README.org
This layer integrates a BitTorrent client into Spacemacs.
Features:
- Integration of Transmission into Emacs.
22.42. Tree-sitter
This layer integrates Emacs Tree-sitter and a few packages built around it.
An Emacs build supporting dynamic modules is required.
Language (i.e. major-mode) support is somewhat limited and varies by feature. Refer to the README/documentation of the package providing the feature for specifics.
Features:
- Syntax highlighting
- Indentation (experimental)
- Folding (experimental)
22.43. Vagrant
This layer adds support for working with Vagrant using vagrant.el and vagrant-tramp.
Features:
- Manage boxes (under the
SPC a t vprefix) - Remote editing on Vagrant boxes via Tramp
22.44. Web-beautify
+tools/web-beautify/README.org
This layer adds support for web-beautify.
Features:
- Format buffer to be beautiful
22.45. Xclipboard
xclipboard integration layer.
Features:
- adds copy support to the X-clipboard from the terminal.
- adds paste support to the X-clipboard from the terminal.
- cliphist package: integration with clipboard managers on Linux and macOS.
23. Vim
23.1. Evil-better-jumper
+vim/evil-better-jumper/README.org
This layer adds support for better-jumper. A configurable jump list implementation for Emacs that can be used to easily jump back to previous locations.
Features:
- jump back and forth
23.2. Evil-commentary
+vim/evil-commentary/README.org
This layer replaces evil-nerd-commenter with evil-commentary for those who prefer the behaviour of vim-commentary.
Features:
- Provides the original vim behaviour for commenting out lines via evil-commentary.
23.3. Evil-snipe
This layer adds various replacements for vim's default search functions.
Features:
- Alternative implementation of vim's default search operations.
- Replacement of evil-surround with a two-character search.
- Support for alternative scopes for default search operations.
- Support for alternative motions based on configurable regexps.
23.4. Vim-empty-lines
+vim/vim-empty-lines/README.org
This layer is a drop-in replacement for the vi-tilde-fringe mode, for those
who desire behaviour closer to vim's.
It has better compatibility with retina displays, as it uses a text overlay
using your font, rather than a pixel-art tilde. The empty line indicators are
overlaid in within the buffer as in vim, and not in the fringe. The indicator
behaviour with trailing empty lines matches vim's behaviour.
For details, see the vim-empty-lines-mode repository.
Features:
- Emulation of original vim behaviour.
- Brings you as close to vim as one can be without using vim itself.
23.5. Vinegar
This layer is a port of vim-vinegar for Emacs.
It is based on tpope's vinegar.vim, simplifying dired
with a limited number of details and exposing the - command in all
buffers to enter dired.
Features:
- navigation up folders with
-key - simplify dired buffer to show only file names
- better evil/vim bindings for navigation within dired buffer
- keep only one active dired buffer
- Use dired-k extension to show time / vcs related information in single bar
- right mouse click moves up directory if in blank space or shows context menu
24. Web services
24.1. Confluence
+web-services/confluence/README.org
This layer adds support for Atlassian Confluence.
Features:
- Creating/editing of Confluence pages
- Exporting of org buffers to Confluence
wikiformat
24.2. Eaf
This layer adds support for the Emacs Application Framework (EAF).
Features:
- Browse using a full-fledged browser within Emacs
- PDF viewer (with continuous scroll)
- Video player
- Image viewer
- See EAF documentation for many more features
24.3. Evernote
+web-services/evernote/README.org
This layer adds support for the famous Evernote note taking service to Spacemacs. It does so by grouping together various packages to work with Evernote.
Features:
24.4. GitHub Copilot
+web-services/github-copilot/README.org
This layer enables usage of GitHub Copilot in Spacemacs using copilot.el.
Features:
- Provide access to ai powered code completions powered by GitHub Copilot
24.5. Hacker News
+web-services/hackernews/README.org
This layer adds support for reading Hacker News.
Features:
- Read Hacker News
24.6. Large Language Model Client
+web-services/llm-client/README.org
This layer enables usage of GPT Clients in Spacemacs using GPTel and Ellama.
Features:
You will have access to the following tools:
- ChatGPT
- Azure
- Ollama
- GPT4All
- Gemini
- Llama.cpp
- Llamafile
- Kagi FastGPT
- Kagi Summarizer
- together.ai
- Anyscale
- Perplexity
- Anthropic (Claude)
- Groq
24.7. Layer for reddit
+web-services/reddit/README.org
This layer adds Reddit support to Spacemacs via the package reddigg. This package allows you to browse reddit in org-mode.
Features:
- Activities on Reddit
- Viewing main
- Viewing sub
- Viewing comments
24.8. Lobsters
+web-services/lobsters/README.org
This layer adds support for reading lobsters.
Features:
- Read Lobsters news
24.9. OpenAI
+web-services/openai/README.org
This layer provides applications to make requests to openai via its API.
Features:
- Provides access to openai via the emacs-openai suite of packages
- Send visual selection or buffer and receive response in current buffer
- Improve, edit, and document code
- Chat sessions with chatgpt
- Obtain AI generated images
24.10. Pocket
+web-services/pocket/README.org
This layer adds Pocket support to Spacemacs via the package pocket-reader.
Features:
- Manage reading list: add, remove, delete, tag, view, favorite, etc.
- Open links in Emacs or external browser
- Sort views by date, title, domain, tags, favorite, etc.
- Search items by keywords, tags, favorite status, unread/archived status, etc.
24.11. Search Engine
+web-services/search-engine/README.org
This layer adds support for the Search Engine package.
Features:
- Browser search integration
24.12. Streamlink
+web-services/streamlink/README.org
This layer adds support for opening URLs in streamlink.
Features:
- Open URL with streamlink
24.13. Twitch
+web-services/twitch/README.org
This layer adds support for twitch. You can search for streamers and open the stream in the browser. You are also able to connect to twitch irc and join the streamer channel.
Features:
- Connect to Twitch irc via erc
- Join streamer channel
- Start watching stream via streamlink
24.14. Twitter
+web-services/twitter/README.org
This layer adds Twitter support to Spacemacs via the package twittering-mode.
Features:
- Activities on Twitter
- Viewing various timelines
- Home timeline
- Replies
- User's timeline
- Public timeline
- Favorites timeline
- Retweets timeline
- Merged timeline
- Timeline without tweets satisfying a condition
- Posting tweets
- Direct message
- ReTweet
- Hash tag
- Signature
- Following and removing users
- Marking tweets as favorites
- Viewing various timelines
- HTTP Proxy support
- Secure connection via HTTPS (cURL, GNU Wget, OpenSSL or GnuTLS is required)
24.15. Wakatime
+web-services/wakatime/README.org
This layer adds support for Wakatime.
WakaTime was built to solve time tracking for programmers. Since we work inside a text editor, why should we have to start and stop a timer? WakaTime uses open-source text editor plugins to automatically track the time you spend programming so you never have to manually track it again!
P.S. wakati means time in Swahili
Features:
- Integration with Wakatime cloud based time tracking service
24.16. Whisper Layer for Spacemacs
+web-services/whisper/README.org
This layer integrates the Whisper speech-to-text tool into Spacemacs, allowing for efficient transcription and audio processing within Emacs.
Features:
- Real-time transcription of audio files.
- Support for multiple languages.
- Selection of different base models for transcription.